Definition Of Mean Free Path In Semiconductor
Mean Free Path m 1 260P cm where P is the pressure Pressuretorr 760 1 01 01 0001 m Cm 626 x 10-6 45 x 10-3 45 x 10-2 045 45 Particle Transport at Low Pressures Above Wafer --- Mean Free Path. Definition of mean free path.
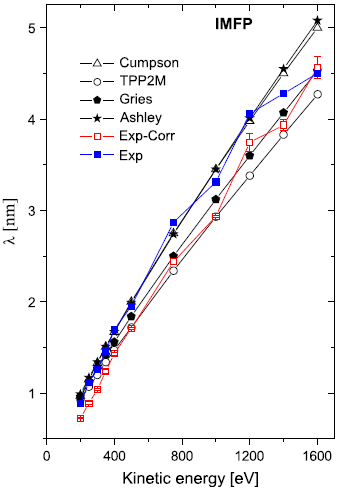
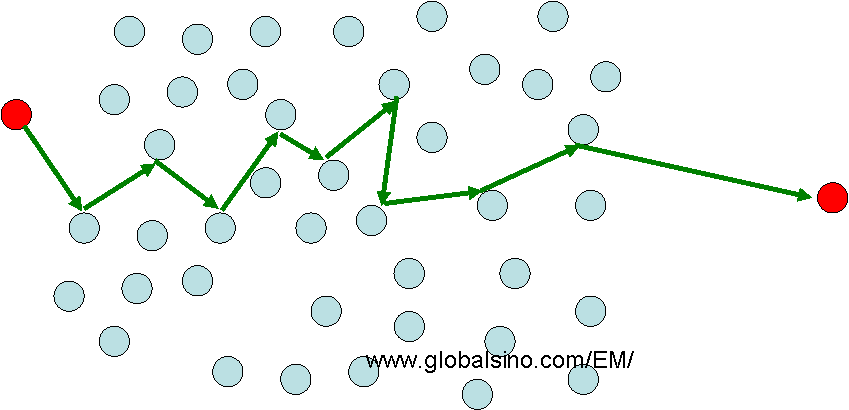 Theory On Inelastic Mean Free Path Imfp Of Electrons
Theory On Inelastic Mean Free Path Imfp Of Electrons
Mean Free Path Device Dimensions.

Definition of mean free path in semiconductor. This motion can be caused by an electric field due to an externally applied voltage since the carriers are charged particles. The average distance traversed between collisions by particles such as molecules of a gas or free electrons in metal in a system of agitated particles. We are giving a detailed and clear sheet on all Physics Notes that are very useful to understand the Basic Physics Concepts.
For particles that can be described by the Maxwellian distribution 3 such as thermal neutrons in a gas under standard conditions the mean free path can be computed from 217 m 1 2 n . Mean free path. We will refer to this transport mechanism as carrier drift.
It is the distance on an average covered by the electron between successive collisions. This motion can be caused by an electric field due to an externally applied voltage since the carriers are charged particles. Mean Free Path Definition Physics.
can be written in terms of mean free path l or . c 10 13s vth 10 7cms1 001m For reference state-of-the-art production MOSFET. Lg 01 m Carriers undergo many collisions as they travel through devices.
E. Average length covered by a charge carrier between two successive collisions in the solid lattice. Mean Free Path Physics Definition Formula Kinetic Theory of Gases.
Moreover the moving particle here refers to a molecule an atom or a photon. Mean Free Path in Semiconductors Semiconductor material has two charge carriers they are electrons and holes. The mean free path has a dependence on the energy distribution of the particles relative to the medium.
The average distance travelled by a molecule between two successive collisions is called mean free path . Oand k are the bulk resistivity and mean free path for electron phonon scattering and d is the relevant length scale that is the wire width or the grain size for surface and grain boundary scattering respectively. Mean free path mhth 110-13 s 22107 cms 2210 -6 cm 220 22 nm This is smaller than the typical dimensions of devices but getting close.
In solid-state physics the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric fieldThere is an analogous quantity for holes called hole mobilityThe term carrier mobility refers in general to both electron and hole mobility. I would like to get an idea about the mean free path of the electrons in doped ZnO thin films. Mean free path refers to the average distance that a moving particle travels between successive collisions or impacts.
Therefore in the limiting case of thin wires andor small grain sizes the wire resistivity becomes proportional to q. Any motion of free carriers in a semiconductor leads to a current. Electron and hole mobility are special cases of electrical mobility of charged particles in.
A motion of free carriers in a semiconductor leads to a current. For this purpose it is useful to define a dislocation mean free path L which is the distance traveled by a dislocation segment of length l before it is stored by interaction with the. In thermodynamics mean free path can be calculated in semiconductor from the measurements on the mobility of electron carrier and electron charge.
Furthermore the successive collisions result in modification of the moving particles energy or direction or any other particle properties. We will refer to this as carrier drift. REVIEW OF MEAN FREE PATH THEORIES In metals and substances with atomic lattices it has been shown Wilson 1936 that if the energy E of an electron above the bottom of the conduction band is small ie.
Term applies also to the motion of species in the gas. mean free path cm vthc Put numbers for Si at room temperature. It is the distance on an average covered by the electron between successive collisions.
This is the case of the classical semiconductor. Is there any formula to calculate the mean free path of the electrons in oxide semiconductor.
 Electron Spectroscopy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Electron Spectroscopy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
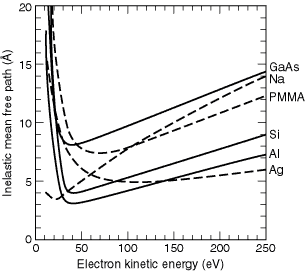 Section 3 2 Electron Ranges In Matter
Section 3 2 Electron Ranges In Matter
 The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
 The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
 Boltzmann Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Boltzmann Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
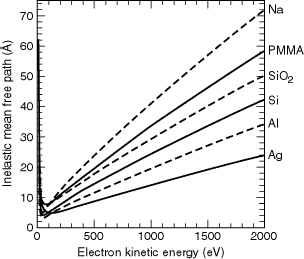 Section 3 2 Electron Ranges In Matter
Section 3 2 Electron Ranges In Matter
 The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
The Dependence Of A Wavelength And B Mean Free Path Heat Spectra On Download Scientific Diagram
 Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Role Of Low Energy Phonons With Mean Free Paths 0 8 Mm In Heat Conduction In Silicon Journal Of Applied Physics Vol 119 No 24
Role Of Low Energy Phonons With Mean Free Paths 0 8 Mm In Heat Conduction In Silicon Journal Of Applied Physics Vol 119 No 24
 Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mean Free Path An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
 Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
 Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram
Electrical Resistivity And The Mean Free Path Of Conduction Electrons Download Scientific Diagram

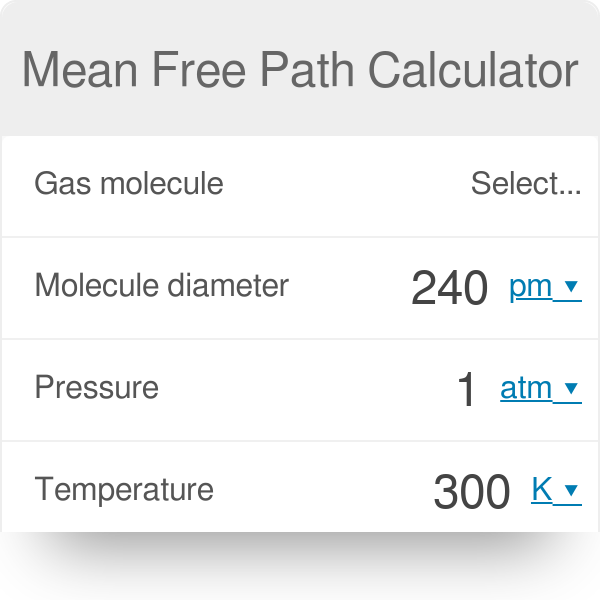

Post a Comment for "Definition Of Mean Free Path In Semiconductor"