What Is Quantum Noise In Radiography
While a deep discussion of quantum mottle is beyond the scope of this section it is worthwhile to know how the noise behaves. When a half-value layer thickness of aluminum is placed into the x-ray beam it reduces the intensi-ty air kerma by 50.
Quantum mottle noise is the only image noise that affects image quality and can be controlled by the radiographer.
What is quantum noise in radiography. Recall that each individual photon is a quantum specific quantity of energy. DETECTIVE QUANTUM EFFICIENCY meani. Partition noise occurring at beam splitters Light with unusual quantum noise properties is called nonclassical light and occurs eg.
Quantum noise quantum mottle. Start studying Image SignalQuantum NoiseScatter Fog Noise. The deterioration of the radiographic image that pertains to the signal What are the two types of image noise.
Techniques Contrast and Noise in Radiography of aluminum in millimeters. Quantum noise or photon noise or short noise or Poisson noise is one considered in detail in the previous section eqs. Figure 1 shows that 03 mm of copper atomic num -.
When more photons are counted in the detector the images will be less noisy. The other primary determinantsof image quality are noise artifacts and contrast. There are very many sources and types of noises also three types are the most common for measurements in the optical spectroscopy applications.
However in order to get more photons counted in the detector the x-ray radiation dose will be higher. This is generally designated quantum noise. Quantum noise also called mottle is the main and the most significant source of noise in plain radiography.
This noise is referred to as quantum mottle. The noise results from random variations in the number of photons the quanta of light that are generated pass through the patient and interact with the detector. The quantum noise mottle noise structural noise and electronic noises are the main sources.
Relationship of Radiation Quantities within an Intensifying Screen-Film Receptor Conversion efficiency is the characteristic of an intensifying screen that is in effect the fraction of absorbed x-ray energy actually converted into light. Noise Noise means random phenomena. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Quantum noise is usually the factor that limits the use of highly sensitive film in radiography. If we increase the dose by N times to the patient noise decreases by square root N times. In all imaging procedures using x-ray or gamma photons most of the image noise is produced by the random manner in which the photons are distributed within the image.
Quantum noise is often a limiting factor for the performance of optoelectronic devices. In the form of squeezed light. In X-ray radiographythere are several randomprocesses.
Noise in virtually all x-ray imaging modalities is dominated by quantum mottle where the latter relates to the total number of x-rays used to generate an image. A typical x-ray beam used in abdominal radiography would likely have an HVL of 3 mm of aluminum. This means that exposing the detector in the absence of an object would result in a grainy image rather than uniform greyscale.
This is due to the photon counting statistics ie. Quantum mottle noise is a result of an inefficient number of photons reaching the imaging plate due to an error in the preset exposure factors mAs and kVp. Noise in plain radiography can be decreased by increasing the mAs which increases the number of photons.
Similarly one may ask what is quantum noise in radiography. In x-ray and CT images the source of noise in the images is referred to as quantum noise or quantum mottle. It is a random process due to fluctuations in the number of photons reaching the detector from point to point.
The number of photonsthat leave the source Poisson The number of those photonsthat pass unaffected throughthe object Binomial. See also Electronic Noise. Radiographic Noise Radiographic noise is a fluctuation in optical density on radiographic or mammographic images often as a result of low radiation dose.
What does DETECTIVE QUANTUM EFFICIENCY mean. Quantum mottle is dominant in all radiography mammography fluoroscopy and CT examinations.
 7 Image Processing Radiology Key
7 Image Processing Radiology Key
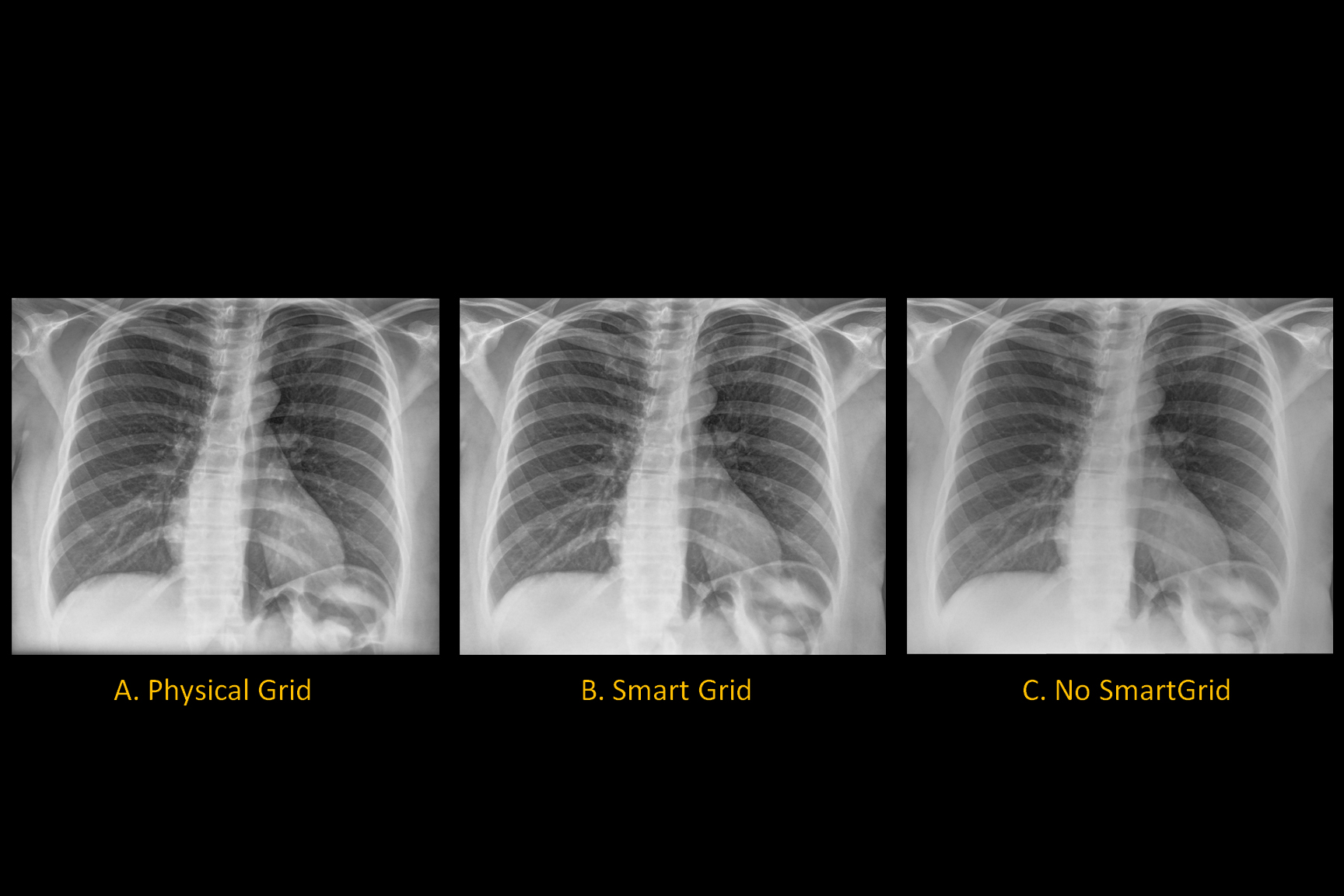
 Optimal Exposure In Digital Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Optimal Exposure In Digital Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
 Radiographic Contrast Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Radiographic Contrast Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Https Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 14 13116
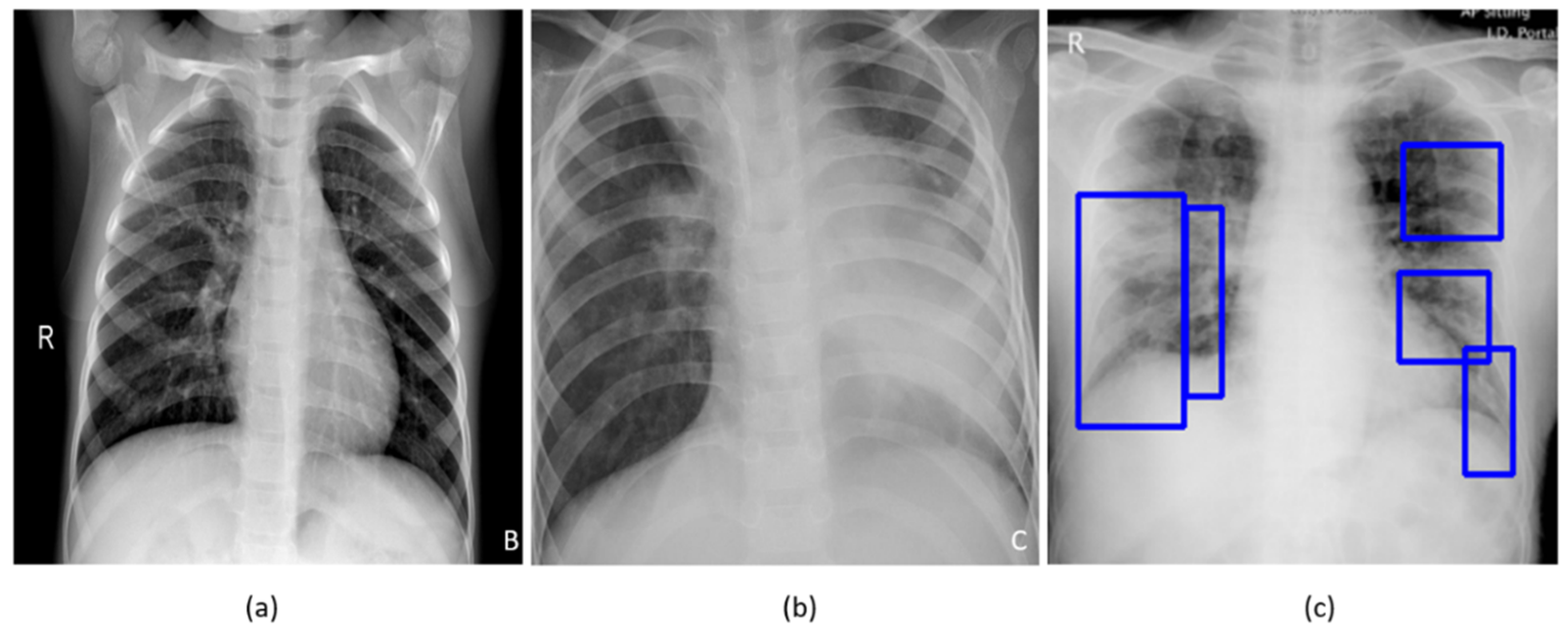 Diagnostics Free Full Text Weakly Labeled Data Augmentation For Deep Learning A Study On Covid 19 Detection In Chest X Rays Html
Diagnostics Free Full Text Weakly Labeled Data Augmentation For Deep Learning A Study On Covid 19 Detection In Chest X Rays Html
Outline And Guide For Learning Image Noise
 Underexposed Vs Overexposed Images A Example Of An Underexposed Image Download Scientific Diagram
Underexposed Vs Overexposed Images A Example Of An Underexposed Image Download Scientific Diagram
 Digital Radiography Flashcards Quizlet
Digital Radiography Flashcards Quizlet
 Image Characteristics Of X Ray Film
Image Characteristics Of X Ray Film
 Radiology Radiology Imaging Radiology Medical
Radiology Radiology Imaging Radiology Medical
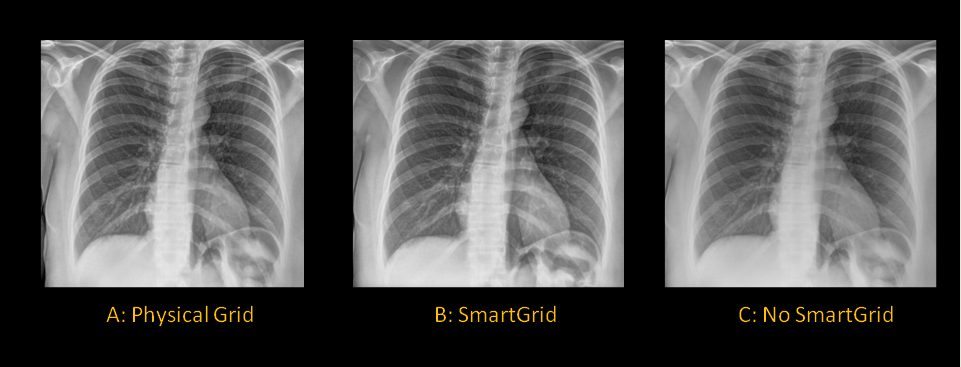 Understanding And Managing Noise Sources In X Ray Imaging Everything Rad
Understanding And Managing Noise Sources In X Ray Imaging Everything Rad
 What Is Quantum Mottle In Radiography Study Com
What Is Quantum Mottle In Radiography Study Com


Post a Comment for "What Is Quantum Noise In Radiography"