Definition Of Wave Energy In Chemistry
A wave is a physical phenomenon characterized by its frequency wavelength and amplitude. Energy can exist in a variety of forms such as electrical mechanical chemical thermal or nuclear and can be transformed from one form to another.
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum For Kids Google Search Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Radiation Visible Light
The Electromagnetic Spectrum For Kids Google Search Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Radiation Visible Light
Molecular Biology and Microbiology for a process or apparatus involving measuring or testing by electrical or wave energy which is separate and apart but in combination with a process or apparatus for use with a viable microorganism or a catalytically active enzyme.

Definition of wave energy in chemistry. In general waves transfer energy from one location to another in which case they have a velocity. A simple example of this is a free particle whose energy eigenstates have wavefunctions that are propagating plane waves. It is sometimes called the spectroscopic wavenumber.
The wave function is a mathematical expression. A disturbance that transfers energy and momentum through space from one region to another even in the absence of any medium in the intervening region. Look it up now.
1 displaystyle tilde nu. For most waves energy is proportional to wave amplitude or the height of the wave The mathematical equation that relates the energy E of light to its frequency is. Standing waves may also occur.
It carries crucial information about the electron it is associated with. In many systems two or more energy eigenstates have the same energy. It turns out that for light the energy of the package of energy is proportional to its frequency.
They have frequency wavelength and amplitude. It is easiest to. Frac 1 lambda where is the wavelength.
The energy of each of these plane waves is inversely proportional to the square of its wavelength. Molecular Biology and Microbiology for a process or apparatus involving measuring or testing by electrical or wave energy which is separate and apart but in combination with a process or apparatus for use with a viable microorganism or a catalytically active enzyme. A wave is a vibration that carries energy with it.
A wave cycle consists of one complete wavestarting at the zero point going up to a wave crest going back down to a wave trough and back to the zero point again. A wave of energy which propagates as a periodic disturbance of the electromagnetic field when an electric charge oscillates or accelerates Amplitude Maximum distance about or below the baseline of a vertical oscillation of an electromagnetic wave-signifies the intensity of the radiation. These have no net velocity and involve no net transfer of energy.
A wave is a periodic oscillation by which energy is transmitted through space. The capacity of a body to do work. From the wave function we obtain the electrons energy angular momentum and orbital orientation in the shape of the quantum numbers n l and ml.
And for a process or apparatus involving electrical or wave energy treatment of a microorganism or an enzyme when the. Energy occurs in several forms-potential as in a compressed spring or a mass in a high position kinetic as in motion chemical as in petroleum and nuclear as in the binding forces of the atomic nucleus. Wavenumber as used in spectroscopy and most chemistry fields is defined as the number of wavelengths per unit distance typically centimeters cm 1.
And for a process or apparatus involving electrical or wave energy treatment of a microorganism or an enzyme when the treatment is. Its effect when manifested is to bring about a change of some kind. All waves are periodic repeating regularly in both space and time.
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between any two corresponding points on adjacent waves. The wave function can have a positive or negative sign. These waves are referred to as electromagnetic waves because they consist of oscillating electric and magnetic waves which you will learn more about in general chemistry.
A wave with a longer wavelength bottom has a lower frequency. The capacity or power to do work such as the capacity to move an object of a given mass in a given direction by the application of force. The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that pass by each second and is measured in Hertz Hz.
 Energy Definition And Types Physics Education Quotes For Teachers Online Tutoring
Energy Definition And Types Physics Education Quotes For Teachers Online Tutoring
 What Is Electromagnetic Spectrum The Word Spectrum Comes From A Latin Word Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Radiation
What Is Electromagnetic Spectrum The Word Spectrum Comes From A Latin Word Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Radiation
 Transverse Waves Examples Of Transverse Waves Physics Tutorcircle Com Wave Theory Physics Longitudinal Wave
Transverse Waves Examples Of Transverse Waves Physics Tutorcircle Com Wave Theory Physics Longitudinal Wave
 1c Wavelengths Crest Trough Distance Learning Targets Learning Waves
1c Wavelengths Crest Trough Distance Learning Targets Learning Waves
 Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Aufbau Principle Wave Function
Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Aufbau Principle Wave Function
 Light Spectrum Google Pretrazivanje Science Images Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum
Light Spectrum Google Pretrazivanje Science Images Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Electromagnetic Waves 21 Gif 450 325 Astronomy Lessons Science Articles School Study Tips
Electromagnetic Waves 21 Gif 450 325 Astronomy Lessons Science Articles School Study Tips
 Wavelength Jpg Jpeg Image 450 285 Pixels
Wavelength Jpg Jpeg Image 450 285 Pixels
 Experiment That Demonstrates The Wave Particle Duality Of Electrons Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Radiation Elementary Particle
Experiment That Demonstrates The Wave Particle Duality Of Electrons Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Radiation Elementary Particle
 1000 Images About Electromagnetic Spectrum On Pinterest Physics Classroom Radio Wave And Physics Electromagnetic Spectrum Physics Classroom Chemistry Help
1000 Images About Electromagnetic Spectrum On Pinterest Physics Classroom Radio Wave And Physics Electromagnetic Spectrum Physics Classroom Chemistry Help
 Definition Wavelength And Frequency Definitions Lesson Frequencies
Definition Wavelength And Frequency Definitions Lesson Frequencies
 1c Waves Speed Equations Waves Longitudinal Wave Learning Targets
1c Waves Speed Equations Waves Longitudinal Wave Learning Targets
 Waves Classwork Homework Classwork Chemical Equation Homework
Waves Classwork Homework Classwork Chemical Equation Homework
 1c Wavelength Frequency Amplitude Characteristics Waves Thedifference Longitudinal Wave Learning Targets Waves
1c Wavelength Frequency Amplitude Characteristics Waves Thedifference Longitudinal Wave Learning Targets Waves
 Wave Motion Ultrasound Physics Apologia Physical Science Writing Skills
Wave Motion Ultrasound Physics Apologia Physical Science Writing Skills
 Igcse Physics 3 3 Define Amplitude Frequency Wavelength And Period Of A Wave Physics Notes Ultrasound Physics Igcse Physics
Igcse Physics 3 3 Define Amplitude Frequency Wavelength And Period Of A Wave Physics Notes Ultrasound Physics Igcse Physics
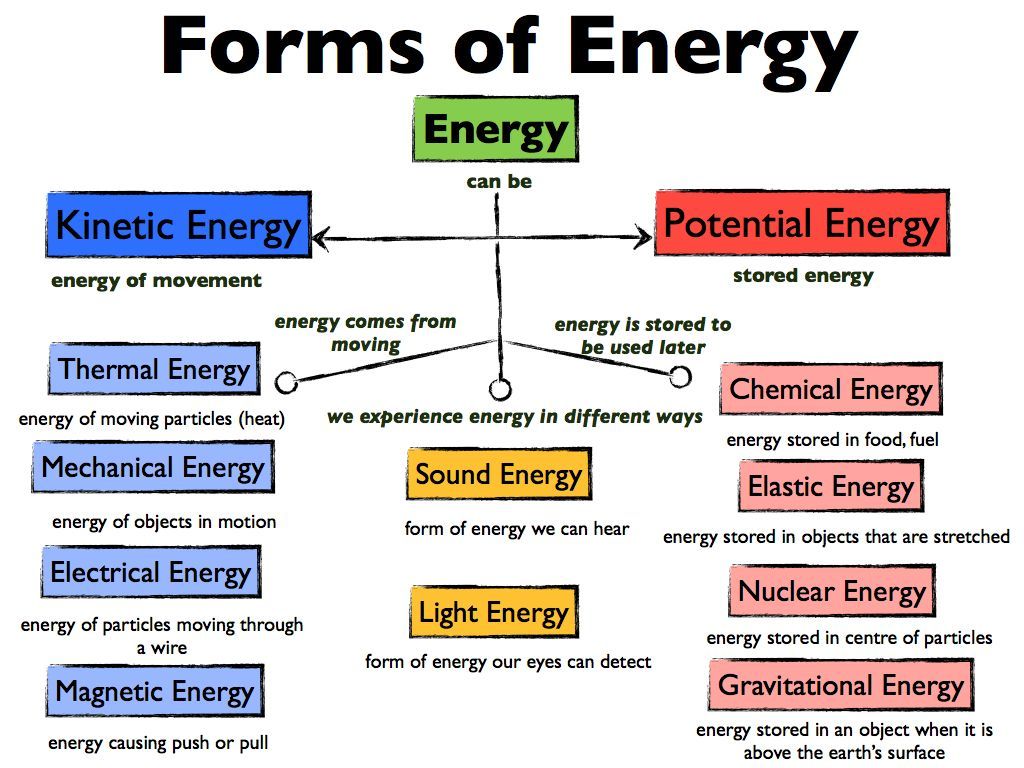 Learning Goal We Are Learning To Explain The Different Forms Of Energy We Encounter Science Lessons Physical Science Experiments Physical Science High School
Learning Goal We Are Learning To Explain The Different Forms Of Energy We Encounter Science Lessons Physical Science Experiments Physical Science High School
 1a Waves Transverse Crest Wavelength Trough Amplitude Waves Anchor Charts Chart
1a Waves Transverse Crest Wavelength Trough Amplitude Waves Anchor Charts Chart
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers Chemistry Worksheets Persuasive Writing Prompts Algebra Worksheets
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers Chemistry Worksheets Persuasive Writing Prompts Algebra Worksheets
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Wave Energy In Chemistry"